MCQ
Why is controlling the output of generative AI systems important?
A. To increase the efficiency of AI models
B. To reduce computational costs
C. To ensure the accuracy of the output
D. To prevent the generation of harmful or offensive content
Answer: D) To prevent the generation of harmful or offensive content
Further Simple explanation for our students and working professionally in detail, read till the last…
Controlling the output of generative AI is mainly done to prevent harmful or offensive content.
AI models can sometimes create biased, false, or inappropriate text, images, or videos. If not monitored, this could spread misinformation or hurt people. By adding safety controls, we make sure AI outputs are safe, respectful, and trustworthy, protecting users and society.
Generative AI systems, like chatbots, Google AI and Image generators, have become increasingly popular due to their ability to create human-like text, realistic images, and even entire pieces of music or art. These systems are built on complex algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data to produce outputs that often appear indistinguishable from those created by humans. However, as powerful as these systems are, controlling their output is crucial for various reasons.
Why Control is Crucial
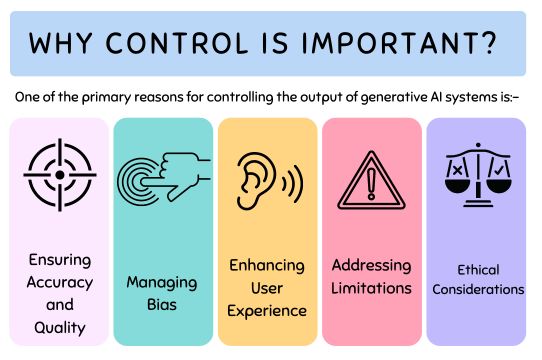
Ensuring Accuracy and Quality
One of the primary reasons for controlling the output of generative AI systems is to ensure the accuracy and quality of the content they produce. Generative AI models rely on the data they are trained on, which means that if the data is flawed or incomplete, the output will likely reflect those shortcomings.
For instance, in the context of natural language processing (NLP), if an AI model is trained on outdated or incorrect information, it might generate content that is factually inaccurate. This can be particularly problematic in applications like automated news writing, education or customer service, where accuracy is paramount.
Moreover, controlling the output helps maintain a consistent quality standard. Without proper controls, the AI might produce content that varies greatly in quality, which can be confusing or even harmful to users. By implementing rigorous quality checks and fine-tuning the models, developers can ensure that the AI’s output meets the desired standards.
Managing Bias
Another critical reason for controlling the output of generative AI systems is to manage and mitigate bias. AI systems learn from the data they are fed, and if that data contains biases—whether related to race, gender, or other factors—the AI will likely replicate those biases in its output.
For example, if an AI model is trained on a dataset that predominantly features male voices, it might develop a bias toward generating male-centric content. This can perpetuate stereotypes and reinforce existing inequalities in society.
By carefully monitoring and controlling the output, developers can identify and address biases in the system, making the AI more fair and equitable. This often involves diversifying the training data and implementing algorithms that can detect and counteract biased outputs.
Enhancing User Experience
Controlling the output of generative AI systems is also essential for enhancing user experience. AI systems that produce unpredictable or inappropriate content can lead to a negative user experience, damaging the reputation of the service or product.
For instance, a chatbot that generates irrelevant or offensive responses can frustrate users and make them less likely to engage with the system in the future. By controlling the AI’s output, developers can ensure that the content generated is relevant, appropriate, and aligned with the user’s expectations.
Moreover, controlling the output allows for personalization, tailoring the AI’s responses to individual users’ needs and preferences. This can create a more engaging and satisfying user experience, encouraging continued use and fostering loyalty.
Addressing Limitations
Generative AI systems, despite their capabilities, have inherent limitations. These systems are not infallible and can sometimes produce content that is nonsensical, irrelevant, or even harmful. Controlling the output helps to mitigate these issues by filtering out or correcting problematic content before it reaches the user.
For example, AI-generated text might sometimes lack coherence or context, leading to confusion or misinterpretation. By implementing control mechanisms, such as content review processes or contextual awareness algorithms, developers can ensure that the AI’s output is coherent, relevant, and contextually appropriate.
Additionally, generative AI systems may struggle with tasks that require deep understanding or creativity beyond the scope of their training data. Controlling the output allows developers to recognize these limitations and guide the AI’s output accordingly, ensuring that it meets the required standards.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of generative AI systems are significant and cannot be overlooked. Without proper controls, these systems can produce content that is misleading, harmful, or unethical. This raises concerns about the responsible use of AI and the potential consequences of allowing AI to generate content without oversight.
For example, AI-generated deepfake videos can be used to spread misinformation or create malicious content that can damage individuals’ reputations or incite violence. By controlling the output, developers can prevent the misuse of AI-generated content and ensure that the technology is used ethically.
Furthermore, ethical considerations extend to issues of transparency and accountability. Users have the right to know when they are interacting with AI-generated content and how that content was created. Controlling the output helps ensure that these ethical standards are met, fostering trust and accountability in AI systems.
Key Considerations for Implementing Controls
Implementing Quality Assurance Processes
To effectively control the output of generative AI systems, it is crucial to implement robust quality assurance (QA) processes. This involves setting clear guidelines for the content that the AI generates and regularly reviewing the output to ensure it meets those standards. QA processes can include both automated checks and human oversight to catch errors or inconsistencies that the AI might produce.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loops
Another important aspect of why is controlling the output of generative ai systems important output is continuous monitoring and establishing feedback loops. By constantly monitoring the AI’s performance, developers can identify patterns or issues in the output that need to be addressed. Feedback loops allow users or stakeholders to provide input on the AI’s performance, which can be used to further refine and improve the system.
Ethical AI Frameworks
Developers should also consider implementing ethical AI frameworks that guide the design and deployment of generative AI systems. These frameworks can include principles such as fairness, accountability, transparency, and respect for user privacy. By adhering to these ethical guidelines, developers can ensure that the AI’s output is not only accurate and high-quality but also responsible and trustworthy.
The Limitations of Generative AI: What’s Holding It Back?
why is controlling the output of generative ai systems important are based on large amounts of data that they are trained on. While this allows them to perform many tasks, their capabilities are still bound by the quality and quantity of the data they’ve learned from.
1. Limited Training = Limited Results
Generative AI only knows what it has been trained on. If it hasn’t seen a particular piece of information or concept, it won’t be able to create something meaningful related to it. For example, if an AI model has never been trained on a specific scientific concept, it won’t be able to generate accurate content around it.
2. No True Understanding of the World
Even though generative AI can produce responses that seem smart, it doesn’t truly “understand” the information it presents. It doesn’t have human-like creativity or the ability to form new ideas. It simply combines what it knows in ways that fit the patterns of data it has learned from.
3. Creativity? Not Quite.
While AI can mix and match ideas in new ways, it can’t create truly original thoughts. It doesn’t know how to come up with a groundbreaking solution to a problem or generate a new idea that’s never been thought of before. It only reuses what it’s learned.
Why These Limitations Matter
These limitations have a significant impact on how and when generative AI should be used. Without controlling the outputs, we might end up with misleading or inaccurate results, which can have serious consequences in many fields like healthcare, law, or education.
1. Risk of Misinformation
If we don’t control or review the AI’s outputs, it might create incorrect or biased information. Since AI doesn’t actually “know” the truth, it might generate plausible-sounding content that is entirely wrong.
2. Ethical Concerns
AI-generated content might unintentionally reinforce harmful stereotypes or biases. For instance, if the training data reflects a biased viewpoint, the AI could spread those same biases in its responses. That’s why controlling what AI generates is important to ensure ethical and fair outcomes.
3. Over-reliance on AI
Some people may mistakenly assume that AI systems can handle everything without human intervention. However, given the limitations, human oversight is still necessary to ensure that the AI is producing accurate and meaningful content.
What Does the Future Hold for Generative AI?
While generative AI has its limitations today, there is a lot of potential for improvement. In the future, we could see AI systems become better at understanding context, refining their ability to generate content that is more creative and accurate.
Here’s what the future might look like:
– Better Training: AI systems could be trained on a wider variety of data, helping them produce more reliable and diverse outputs.
– Improved Creativity: With advancements in AI, there’s hope that systems could one day generate more original ideas, possibly even solving problems in innovative ways.
– Enhanced Control Tools: New tools could allow users to better control and filter AI outputs, making sure the content is accurate, unbiased, and ethical.
More Limits of Generative AI: Human Oversight is Key
Even though AI is improving every day, human oversight will always play a critical role. Humans bring creativity, ethics, and reasoning to the table—things that AI can’t replicate. The combination of human insight and AI’s capabilities could be a powerful tool for the future, but we must remember that AI is here to assist, not replace human judgment.
Conclusion
Controlling the output of generative AI systems is essential for ensuring that these powerful tools are used effectively, ethically, and responsibly. By focusing on accuracy, quality, bias management, user experience, and ethical considerations, developers can create AI systems that are both beneficial and trustworthy.
As generative AI continues to evolve, the importance of controlling its output will only grow. By implementing robust controls and ethical guidelines, we can harness the full potential of generative AI while minimizing its risks and limitations.
FAQ
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can create new content, such as text, images, or music, based on the data they have been trained on. These systems use complex algorithms to analyze patterns in the data and generate outputs that mimic human creativity.
Controlling the output is crucial to ensure the accuracy, quality, and ethical integrity of the content produced by generative AI systems. It helps prevent the spread of misinformation, manage biases, and enhance user experience.
Output can be controlled through various methods, including quality assurance processes, continuous monitoring, feedback loops, and ethical AI frameworks. These controls help ensure that the AI’s output is accurate, relevant, and aligned with ethical standards.
Ethical concerns include the potential for AI-generated content to spread misinformation, reinforce biases, or be used maliciously (e.g., deepfakes). Transparency, accountability, and fairness are key ethical considerations when using generative AI.
By ensuring that the AI generates relevant, accurate, and appropriate content, user experience is improved. Controlled output also allows for personalization, making interactions more engaging and satisfying for users.
Generative AI systems can produce content that is nonsensical, contextually inappropriate, or biased if not properly controlled. They may also struggle with tasks requiring deep understanding or creativity beyond their training data.
I’m a passionate AI enthusiast and the founder of AI UPSURGE. With a deep interest in the latest developments in artificial intelligence, I’m dedicated to making AI accessible and understandable for everyone. Through insightful articles, practical guides, and aims to empower readers to harness the power of AI in their daily lives and professional endeavors. When not writing or exploring the latest AI trends.